The Internet
The Internet might seem intimidating at first. – A vast communications network spanning the globe with billions of web-pages that are made to satisfy and inform their constituents. Indeed the Internet is quite large with many “pages.” However, in this lesson we will simplify the Internet to allow you to become masters of it.
The Internet, the web, cyberspace, and the ‘net are all terms that generally mean the same thing, in this case, we will call it the Internet. The Internet is a NETwork of computers, all over the world, INTERconnected to each other and available to any individual. The Internet is used for many different activities including shopping, communicating, learning, and distributing information.
Unfortunately, you cannot open a door to a house, and expect to “go into the Internet.” Computers are primarily the tool you utilize to use the Internet. The Internet is somewhat difficult to describe because you cannot touch it. Sometimes it is best described in comparison to a library. The Internet is made up of many individual components, just like a library is made up of many books. The Internet’s components have even more individual parts, just like a book has pages.
Changing Constantly
Because information, such as news, sports, and money, changes so quickly in this day and age, the Internet must change along with it. This might seem confusing. However, it is not necessarily so. The Internet can be thought of as a dynamic living organism that changes and adapts to its environment. Thus, one web “page” that you saw yesterday, might be gone the day after tomorrow.
Purpose/Content of Websites
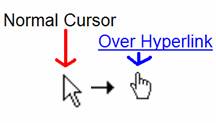
On the Internet, there are many web sites. These are usually made for one specific purpose; it might be telling you the news, or it might be informing you on the benefits of stamp collecting. The best analogy for a web site is probably a comparison to an entire book, or an entire newspaper. Web Sites are made up of “pages,” just like a newspaper or book. Web sites are usually independent, however sometimes linked together by hyperlinks (also called links) that allow you to jump from one web site, to another website. These links allow you to “turn the page,” and move around on the Internet. They are usually underlined and blue, however they can be any color and sometimes even can be a picture. How to identify a hyperlink – when your mouse hovers over a hyperlink, the arrow changes into a pointing hand.
These pages are what you see and read on the Internet. They are primarily made up of text (words), digital media, (pictures, movies, music) and hyperlinks. The Internet, unlike a book or newspaper, is in no order, and thus, at times, can seem slightly confusing. However, there are tools on the Internet that fortunately organizes it and allows you to use it comfortably and easily.
Applications to Access the Internet
On the computer, you use an application, or program, to see the Internet. This is called a web browser – you “browse” the web with it. Some common web browsers include Internet Explorer, Netscape, Firefox, and Mozzila. There is no major difference between these, however, they look a little different, and appeal to different Internet users. They share a common purpose, to navigate the Internet, and have basically the same buttons. (Collectively, buttons make a toolbar) For instance, we will take a look at the buttons of Internet explorer. You use these buttons to also help you navigate the Internet:
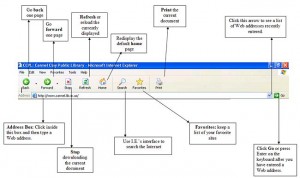
Each button has a specific purpose:
Back Button – This button allows you to go back to the previous page that you were at. It is the most used and if you accidentally click a link, this is the button you would use to get back to where you were.
Forward Button – If you accidentally clicked back, you don’t have to hunt for the hyperlink on the webpage to go back to the previous page.
Stop Button – If the webpage you are loading takes a long time to load, and you are in a rush, you can click this button to make it stop loading. This is very useful if you are looking at many pictures. Pictures take up a lot of space on the Internet, and it takes a long time for them to be transported from the Internet onto your computer. Thus, you can conveniently use the stop button.
Refresh Button – This button is especially useful if you are looking up the news, sports scores, or the weather. By pressing the refresh button, the web page is loaded again, and also updated. (Very useful for websites that change a lot i.e. news, sports, weather, etc.)
Home Button – When you open your Web Browser, the first website that is displayed is your home page. This web page is called your home page. It is essentially the first page you come to when you open your web browser. You can change your homepage to your preferences. When you press the home button, it takes you to your home page.
Search Button – the search button is another way of looking up something on the Internet.
Favorites Button – This loads a panel that lists all of your pre-programmed favorite websites.
Address Box – This displays the URL of a webpage. URL stands for Universal Resource Locator. It is essentially an address for the webpage. Each URL is unique for the webpage. You can type a specific URL into the address box by left clicking in it once and then typing. Although URLs are all different, they share common characteristics. The basic diagram of a URL is shown below:
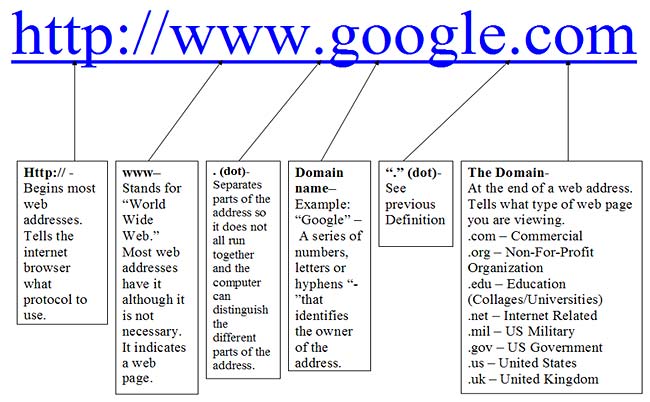
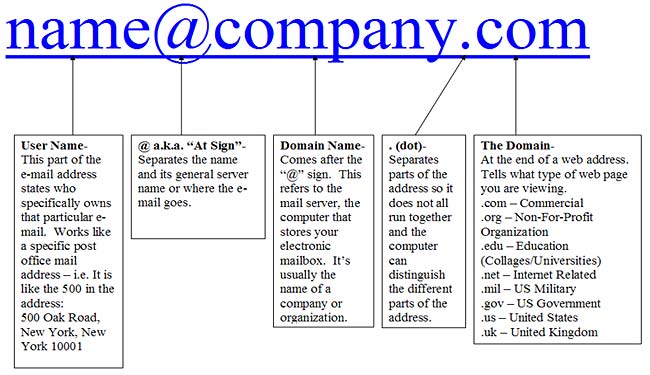
This is different than an E-mail (Electronic Mail) Address, which we will get into later:
Scrolling – Again!
 One thing to keep in mind when viewing the Internet is that a bunch of information might be displayed on a webpage, however, only a small portion can be seen immediately when you load the webpage. Thus, it is important to look at your scroll bars to the right and bottom to see if there is more information you are missing. If you are tired of using the mouse to scroll up and down, try using the arrow keys. These are easier to manipulate.
One thing to keep in mind when viewing the Internet is that a bunch of information might be displayed on a webpage, however, only a small portion can be seen immediately when you load the webpage. Thus, it is important to look at your scroll bars to the right and bottom to see if there is more information you are missing. If you are tired of using the mouse to scroll up and down, try using the arrow keys. These are easier to manipulate.
Aggravations!
On the Internet, there are things that help you, and things that can make you aggravated. One aggravation is the Pop Up Ad. These irritating advertisements are caused by aggressive marketers who want you to see their “amazing” product and buy it. Pop ups create their own window and usually appear on top of the information that you are interested in. How irritating! If you click on these, they will take you away from the information you are looking at, and direct you to a phony website that tries to steal all of your information or hurt your computer. The simple solution to these menacing advertisements is not falling for the phony outrageous deals they are advertising by clicking the X at the top right of the window immediately. Another type of advertisement is the Banner. Unfortunately, banners cannot go away. They are on web pages and are there to stay. Just like Pop ups, they are used by marketers to sell phony items and usually damage your computer if you click on them. Be careful not to click on them and the only solution to them is to ignore them.
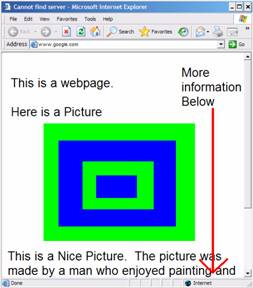
Another unfortunate webpage that you might come across on the Internet, is that sometimes, when you go to a webpage, you might come up with a screen that looks like this:

This essentially means that a website has either disappeared, been deleted, or is unavailable. Sometimes try clicking on the refresh button in the toolbar, and the web page may load. Other times it may not. This error may also be caused by an incorrect typing of a URL. If you manually entered the URL, try double-checking to make sure you spelled it correctly, or if you accidentally used a comma instead of a period. Unfortunately, if these solutions don’t work, you might be out of luck!
Web traffic is a common thing on the Internet. Sometimes, a website can become very sluggish or inaccessible because too many people are trying to visit the website. This is just like too many people crowding the highway at rush hour when they all are trying to get home! Heavy web traffic usually occurs during the early evening hours, when many people get home from school or work. It is a good idea to not surf during these hours, or you might wait quite some time to visit a web page. If traffic is too severe, web pages might display a “404 Page Not Found” sign that encourages you to try again later. Unfortunately, there is nothing that you can do to stop this.
Congratulations! You have now passed the basic principles of the Internet. Now it is time to find out more about what you can do on the Internet. – E-mail is coming up soon!
Internet Searching
On the Internet, there are websites specifically designed to help you find websites and organize them. These are called Search Engines and Subject Directories. We shall explore two of these.
Google
www.google.com
Google is a search engine, a Web site used to search for information on the World Wide Web. Google collects Web sites using a computer program (called a wanderer, crawler, robot, worm, or spider). Google then creates an index of these sites that you can search.
Use a search engine when
- you have a narrow topic or idea to research
- you want to retrieve a large number of Web pages on a topic
- you want to search for information from a particular type of site or domain (.org, .gov, .edu)
- you want to retrieve certain file types (e.g., images, audio, video)
- you want to retrieve pages in other languages
Performing a search in Google
- Think of keywords to use in your search.
- Click inside the search box with the mouse, then type in your keywords.
- Click the “Google Search” button or press the Enter key on your keyboard to start the search.
- To view a site in the list of results, click on the blue underlined title of the site.
Google searching tips
- Google will return pages that include all of your search terms. There is no need to include the word “and” between terms. For example, to look for information about parks in Cincinnati, simply type Cincinnati parks.
- Google is not case sensitive. Typing reggie miller is the same as typing REGGIE MILLER or Reggie Miller.
- The “I’m Feeling Lucky” button will take you directly into the first Web site on the list of results.
- The more words you include in your search, the more specific your search will be.
- If you don’t find what you need in the first 20-30 sites, try another search engine.
Use Google’s Advanced Search when you want to
- search for a phrase
- exclude words from your search
- find pages in a specific language
- find pages from a particular type of site or domain (.com, .org, .gov, .edu)
- search for images
Yahoo!
www.yahoo.com
Yahoo! is a subject directory, a Web site that offers a collection of links to Internet resources submitted by site creators or evaluators and organized into subject categories. Most subject directories are searchable.
Use a subject directory when
- you have a broad subject, or just want to browse.
- you want to see a list of sites on your topic often recommended and annotated by experts.
Two ways of searching Yahoo!
- Using the categories, you can find information by browsing through each subject.
- Click on the category you wish to search.
- Follow the categories by clicking on the links until you find the information you want.
- By entering keywords into the search box, you can make your way quickly to any of Yahoo’s categories.
- Think of keywords to use in your search.
- Click inside the search box with the mouse, then type in your keywords.
- Click the “Search” button or press the Enter key on your keyboard to start the search.
- To view a category or Web site in the list of results, click on the blue, underlined title.
Yahoo! searching tips
- Results from your search are presented on the “search results” page with links to Yahoo! categories first and then to individual Web site matches.
- Links to Yahoo! categories are in bold faced type. Links to Web sites outside Yahoo! are not in bold.
________________________________________
Try these questions to test your searching skills using Google or Yahoo!
- Look for recipes that use eggplant.
- Browse for Web sites about container gardening.
- Find the lyrics of the official state song of Indiana.
- Browse for Web sites about harps.
- What is the phone number of the Office of Admission at Otterbein College?
- The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has useful information on travelers’ health issues. Can you find this information without knowing the Web address for the agency?
Hint: To find specific information, a search engine works best. Browsing is easiest in a subject directory.
Helpful Internet Links
Popular Search Engines and Subject Directories
Google – www.google.com
Dogpile – www.dogpile.com
Bing – www.bing.com
Yahoo – www.yahoo.com
Vivisimo – www.vivisimo.com
Free E-Mail Accounts on the Web
Yahoo! – mail.yahoo.com
Live – www.live.com
Google Mail – Gmail – www.gmail.com
Other Useful Sites
Search Engine Watch – www.searchenginewatch.com
Lists and descriptions of search engines as well as search engine updates.
Symantec AntiVirus Research Center – www.Symantec.com/avcenter/hoax.html
Information about viruses and hoaxes.
Webopedia – www.webopedia.com
An online dictionary for computer- and Internet-related terminology.
Glossary of Internet Terms
Browser – A software program that allows Internet documents to be viewed, also called a Web Browser.
Cyberspace – The world of computer networks.
Domain Name – A unique name that identifies a specific computer on the Internet.
Download – A term for transferring software or other files from one computer to another.
E-mail – Electronic Mail – Messages sent from one specific user to another using a network
E-mail address – The way a specific user is identified so that they may receive E-mail. An e-mail address can be identified by the “@” sign. E.g., [email protected]
Hits – The number of files downloaded from a computer on the Internet, or the results of a query performed with a Search Engine.
Home Page – The first page of a Web Site, similar to a table of contents.
HTML – HyperText Markup Language- A computer language used to make hypertext documents that are sent via the World Wide Web and viewed using a Browser.
HTTP – HyperText Transfer Protocol – The way that hypertext documents are transferred over the Internet.
Hypertext – A way of presenting information that allows words, pictures, sounds, and actions to be inter-linked so that you may jump between them however you choose.
Link – A highlighted word, phrase, or image that allows you to jump to another document on the World Wide Web.
Metasearch Engine – Allows one to search several search engines at one time.
Search Engine – a web site that indexes and allows searching of information gathered from the Internet.
URL – Uniform Resource Locator – The entire address for a piece of information of the Internet. E.g., www.yahoo.com
Web Page – a hypertext document available on the World Wide Web.
Web Site – A collection of Web Pages.
World Wide Web – A collection of resources available on the Internet using a Web Browser.